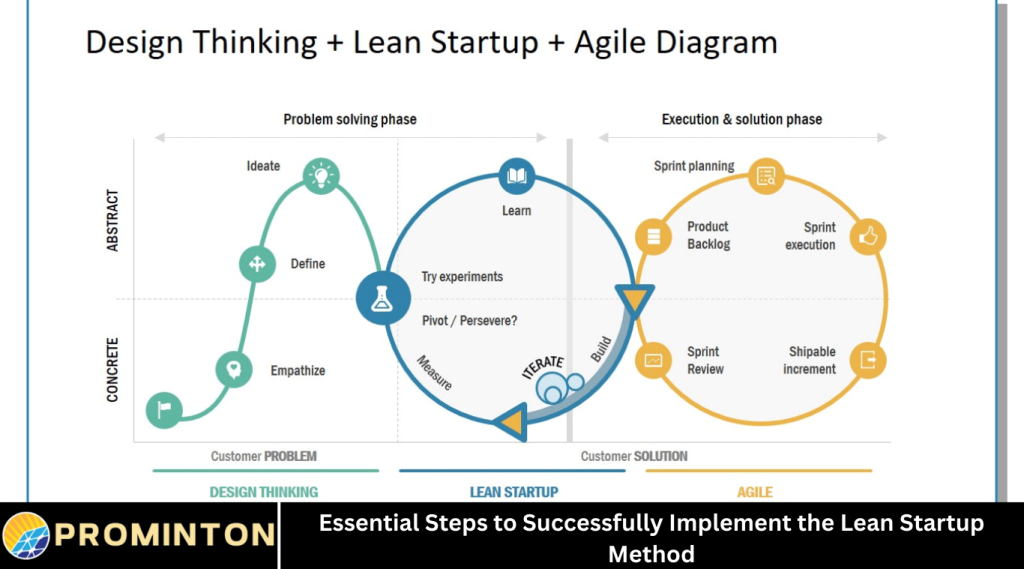
Starting a new business can be exciting but challenging. Many startups fail because they do not manage their resources well or misunderstand their customers’ needs. The Lean Startup Method is a popular approach that helps entrepreneurs build businesses more efficiently by focusing on learning, testing ideas quickly, and adapting based on feedback.
This article will explain the essential steps to successfully use the Lean Startup Method. It will guide you on how to create a minimum viable product, test your assumptions, collect feedback, and improve your business. Whether you are just starting or looking to improve your existing startup, this guide will help you apply lean principles and increase your chances of success.
Understanding the Lean Startup Method
The Lean Startup Method is based on the idea that startups succeed by learning what customers really want early in the process. Instead of spending a long time building a perfect product, lean startups build a simple version first. This simple version is called a minimum viable product, or MVP.
By releasing the MVP quickly, startups can gather real customer feedback. This feedback helps them understand if their idea works or needs improvement. Then, they make changes, learn more, and repeat the process. This cycle is called “build-measure-learn.”
The goal is to avoid wasting time and money on products that customers do not want. The Lean Startup Method encourages entrepreneurs to be flexible and adapt based on real market data.
Identifying Your Assumptions and Hypotheses
Before you start building your product, it is important to identify your key assumptions about the business. These assumptions might include who your customers are, what problems they have, and whether they will pay for your solution.
Write down your hypotheses clearly. For example, you might assume that customers want a faster way to order food online. These hypotheses will guide your testing and product development.
Being aware of your assumptions helps you focus on what needs to be tested first. The goal is to validate or invalidate these ideas as early as possible.
Creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP is the simplest version of your product that allows you to test your main hypotheses. It should have just enough features to solve the basic problem for early customers.
Building an MVP quickly helps you get your idea in front of real users. Avoid trying to make it perfect or adding many features at this stage. The goal is to learn, not to impress.
For example, if you want to build a new app for ordering groceries, your MVP might be a simple website that allows users to select items and place an order. You can test if customers like it before adding extra features.
Testing Your MVP with Real Customers
Once your MVP is ready, it’s time to test it with actual users. This step is critical to understanding how customers react to your product and whether it solves their problem.
Collect feedback by observing how customers use the product, asking questions, and reviewing their comments. Look for patterns in what they like and dislike.
Testing helps you see if your assumptions were correct or if you need to make changes. Be open to criticism and ready to learn from your customers.
Measuring and Analyzing Data
Data is a key part of the Lean Startup Method. After testing your MVP, collect data on user behavior, sales, and other important metrics.
Use simple tools to track how many people use your product, how often they return, and whether they pay for it. Analyze this information to make informed decisions.
By measuring results, you avoid guessing and can focus on changes that will have the biggest impact.
Learning and Pivoting Based on Feedback
Learning means using the information from your tests to improve your business. Sometimes, the feedback will confirm your original idea. Other times, it will show you that your assumptions were wrong.
If the data suggests a different direction, you may need to pivot. Pivoting means changing your product, target market, or business model to better meet customer needs.
Being willing to pivot quickly saves resources and helps you find a more successful path.
Iterating the Build-Measure-Learn Cycle
The Lean Startup Method is not a one-time process. It involves continuously repeating the cycle of building, measuring, and learning.
Each iteration helps you improve your product and business model. Over time, you develop a better understanding of your customers and what works.
Staying committed to this cycle allows you to grow your startup sustainably and reduce risks.
Focusing on Customer Development
Customer development means actively engaging with your customers to understand their needs and problems.
Talk to customers regularly, observe their behavior, and ask for feedback beyond just your product. This helps you discover new opportunities and adjust your strategy.
Customer development ensures your startup remains customer-focused and responsive to changing demands.
Managing Resources Efficiently
Lean startups often have limited resources. It is important to manage time, money, and people efficiently.
Prioritize activities that directly contribute to learning and growth. Avoid spending on unnecessary features or marketing before your product is ready.
Using resources wisely helps extend your startup’s runway and increases your chances of success.
Building a Lean Startup Culture
A lean culture encourages experimentation, learning from failure, and continuous improvement.
Encourage your team to share ideas, test new approaches, and be open about challenges.
A positive culture helps startups adapt quickly and stay motivated.
Using Lean Startup Tools and Techniques
Several tools can support the lean process. For example, customer interviews, surveys, A/B testing, and analytics platforms.
Choose tools that fit your needs and help you gather real data.
Using the right tools makes testing and measuring easier and more accurate.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing the Lean Startup Method can be difficult. Challenges include fear of failure, impatience, and difficulty interpreting data.
To overcome these, stay focused on learning rather than success or failure. Be patient and trust the process.
Seek advice from mentors or join startup communities for support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Lean Startup Method?
The Lean Startup Method is an approach that helps startups develop products quickly by building a simple version first, testing with customers, and learning to improve.
Why is a minimum viable product important?
An MVP allows you to test your main ideas with real users quickly and cheaply, helping you learn what works before investing more resources.
How do you know when to pivot?
You pivot when customer feedback and data show that your current product or strategy is not meeting market needs, and a change is needed to succeed.
How can startups collect useful customer feedback?
Startups can collect feedback through surveys, interviews, observing user behavior, and analyzing product usage data.
What are common mistakes when implementing the Lean Startup Method?
Common mistakes include building too much before testing, ignoring customer feedback, and not measuring results properly.
How often should startups iterate the build-measure-learn cycle?
Startups should iterate as often as possible, making small changes based on feedback and data to continuously improve their product.
Can the Lean Startup Method be used by established businesses?
Yes, established businesses can use lean principles to develop new products, test ideas quickly, and stay responsive to customer needs.
Conclusion
The Lean Startup Method offers a practical way for entrepreneurs to build businesses that customers want. By focusing on early testing, learning, and adapting, startups can save time and money while improving their chances of success.
The essential steps include identifying assumptions, building a minimum viable product, testing with customers, measuring data, learning from feedback, and iterating the process. Managing resources wisely and fostering a lean culture also play important roles.